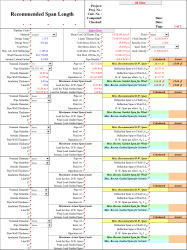
Recommended Span Length
Description
This spreadsheet is calculating recommended pipe support spacing for piping systems - essentially determining how far apart you can place pipe supports before the pipe starts to sag too much or experience excessive stress.
Main Engineering Principle
Think of this like determining how far apart you can space the legs under a table before the tabletop starts to bend under its own weight. The pipe acts like a beam spanning between supports, and several factors determine the maximum safe distance:
Key Considerations:
- Pipe weight - The pipe itself has weight that creates downward force
- Fluid weight - The liquid inside adds significant additional weight
- Insulation weight - Any insulation wrapping adds more load
- External forces - Wind pushing sideways and seismic (earthquake) forces
- Temperature effects - Hot pipes expand and create thermal stresses
Multiple Span Calculations: The spreadsheet calculates different maximum spans for different scenarios:
- Deflection-based spans - How far before the pipe sags too much (comfort/appearance)
- Stress-based spans - How far before the pipe material is overstressed (safety)
- Wind spans - Spacing for supports that guide against wind loads
- Seismic spans - Spacing for supports that handle earthquake forces
The calculation follows established piping codes (ASME B31.1) and structural engineering principles to ensure the piping system is both safe and functional. The actual span chosen would typically be the most restrictive (shortest) of all these calculated values.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.